A VM shared disk on Microsoft Cluster Service (MSCS) is running out of disk space. The VMs are on a single host (aka cluster in a box - CIB). I can think of two ways to expand the disk storage.
- create a new big shared disk for the cluster, migrate the data, then change the new disk to the same drive letter as the original disk
- extend the size of the existing shared disk
Obviously the latter seems simpler, but it requires special attention. The shared disk format in MSCS VMs must be in eager zeroed thick format. However, when extending an eagerzeroedthick VMDK, the extended chuck is in lazy zeroed thick format by default (reference “Extending an EagerZeroedThick Disk”. In my test, vSphere 6 has the same behavior)
Here is how I extend the MSCS shared disk
- Power off both servers in the cluster
- Increase the VMDK disk size. There are two ways:
- GUI: edit the VM settings, increase the shared disk size
- CLI: use vmkfstools -X <newsize> -d eagerzeroedthick <vmdkfile>
- For more info about vmkfstools, see my vmkfstools Examples post
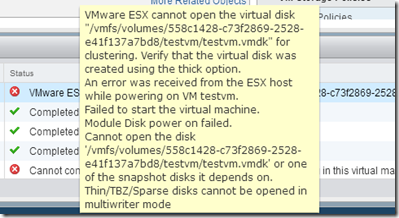
- Using the GUI, the extended chuck will be in lazy zero thick format. The VM will fail to power on with the error “VMware ESX cannot open the virtual disk for clustering…”
- There are two ways to convert the extended chuck to eagerzeroedthick format
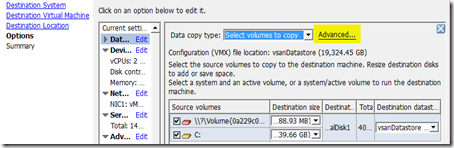
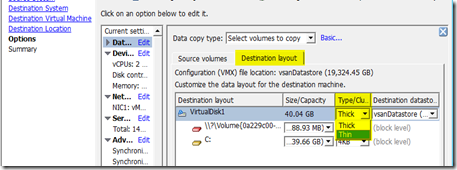
- Migrate the VM to another storage, and specify the eager zero thick format for the disk
- Use vmkfstools -k <vmdkfile>
- Once the entire shared disk is the eager zeroed thick format, the VM will be able to power on.
- Extend the Windows partition as KB304736