vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) 6.5 comes with the built in backup functionality. Starting a backup is quite easy - login the vCSA web console and click Backup button on the Summary page (see
this post for the step-by-step screen shots).
Even it looks a very simple task, I have learned a few lessons when configuring the vCSA backup.
Lesson #1: vCSA backup location is <host_name>/<folder_name>If using FTP protocol, the backup location is not just the FTP server host name or IP address; it MUST include the folder name. There is a “/” between the host name and folder name.
Otherwise, the error message is “FTP location is invalid”.
 Lesson #2: vCSA backup supports the FTP virtual host name if entering the username correctly - <ftp virtual hostname>|<ftp username>
Lesson #2: vCSA backup supports the FTP virtual host name if entering the username correctly - <ftp virtual hostname>|<ftp username>See my Lesson #2 in “
Setting Up IIS 8 FTP Server Lessons Learned” about the FTP virtual host name login. There is a “|” between the hostname and username.
Otherwise, the error message is “Access to the remote server is denied. Check your credentials and permissions”.
 Lesson #3: Use curl to troubleshoot vCSA backup error
Lesson #3: Use curl to troubleshoot vCSA backup errorAfter entering the correct settings, vCSA backup wizard validates the settings and starts the backup. The backup fails with “BackupManager encountered an exception. Please check logs for details”, but it does not provide much details or the location of the log file.
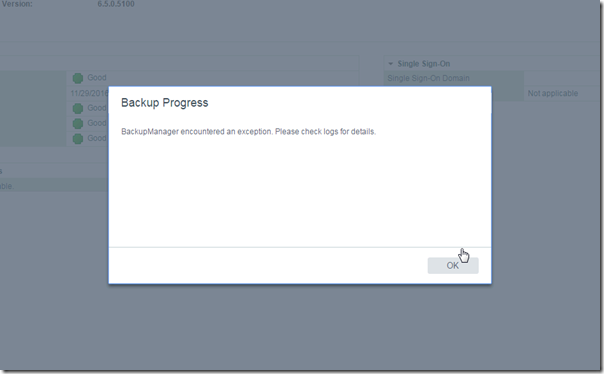
After some digging, I found the backup log file in
/var/log/vmware/applmgmt/backup.log. In the log file, there is a curl error “Connection time-out”.
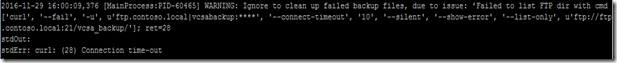
This gives me a hint that vCSA backup uses curl to transfer the backup file from vCSA to the FTP location. Recently I am also learning curl to transfer file, so I’m a little familiar with curl. (I will publish what I learn from curl in a future post).
From vCSA console, enter “
curl -u <ftp user>:<password> -l <ftp server>”. It should list the file and directory on the FTP server. But I got the timeout error. I also tried running curl on a Windows computer, and got the timeout error too. This leads to me think the problem is on the FTP server. Finally the fix is to restart the FTP service (see Lesson #1 on “
Setting Up IIS 8 FTP Server Lessons Learned”).
I am not sure why the wizard was able to successfully validate the FTP server setting when the FTP server connection is blocked by the Windows Firewall. When troubleshooting the Windows Firewall, I thought I could use the FTP command to connect to the FTP site, but using curl would fail. I’m not 100% sure about this, since I can’t replicate the issue again. After restarting the Microsoft FTP service, everything is working okay.
Anyway, using curl is the best tool to troubleshoot the vCSA backup failure.
Lesson #4: vCSA backup location must be an empty folderAfter successfully running a backup, I try running the backup one more time with the same setting. I got the following error. (PS. In the screenshot below, I removed the virtual hostname on the FTP site, so I can just use the username).