I always think when creating or migrating VM on a VSAN datastore, its disk should be thin provisioned. However, I discovered some VM disks in our VSAN datastore are “thick” provisioned even all the VM storage policies are set to 0% object space reservation. How is it possible? After some digging, here is what I learn.
Thick Disk Format on VSAN
VSAN defines the disk type (thin or thick) via the Object Space Reservation setting in the VM Storage Policies. By default, this value is 0%, implying the disk is deployed as thin.
If the value is set to 100%, meaning the space for the disk is fully reserved, which can be thought of as full, thick provisioned. This behaves similarly to thick provision lazy zeroed. There is no eager-zeroed thick format on VSAN. (reference: Virtual SAN 6.2 Design and Sizing Guide, page 65)
Benefit to Provision Thick Disk on VSAN
Based on my understanding of VSAN disk IO operating (VSAN mirrors write IOs to all active mirrors, there are acknowledged when they hit the flash buffer!), typically there is no performance difference between thin and lazy zeroed thick provision on VSAN. Remember, there is no eager-zeroed thick format on VSAN (see above). Also see the Yellow-Bricks post. (PS: Duncan’s post may misspeak about VSAN eager zero thick provision.)
Provision Thick Disk on VSAN (Intentionally or By Accident)
There are several possible ways to provision a thick disk on VSAN.
- Possibility #1
- Define a thick VM Storage Policy
- Set the Object Space Reservation to 100%
- Use vSphere Web Client (cannot use vSphere C# Client)
- Select the thick VM storage policy
- Possibility #2
- Use vSphere C# Client
- Select “Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed” or “Thick Provision Eager Zeroed” on the disk type
- I don’t know what the actual impact on VSAN when selecting eager zero. In my test, the VM disk is still created correctly. I will do more research and post an update.
- Possibility #3
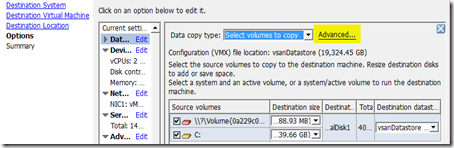
- P2V a physical server to VM
- By default, P2V uses thick provision on the disk
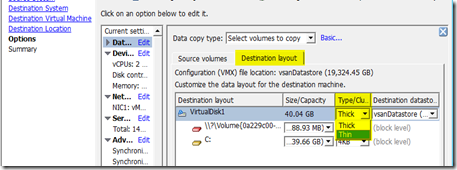
- Change to Destination Disk to thin provision by select Advanced, Destination layout, Type, Thin
- For VSAN 5.5, there is one more method, see here.
Change Thick Provisioned Disk to Thin on VSAN
Unfortunately, there is not a simple way to change a thick provisioned disk to thin on VSAN. Simply changing the VM storage policy on the disk has no impact.
In order to convert a thick disk to thin provisioned, do a storage migration of the disk to a SAN / NFS / local storage, then migrate back to the VSAN datastore. Make sure select the thin provision storage policy during the migration.